Trilateral Highway: The silver lining
Keywords - Moreh, India, Myanmar, Thailand, ASEAN, Northeast Region, Border Trade
Introduction
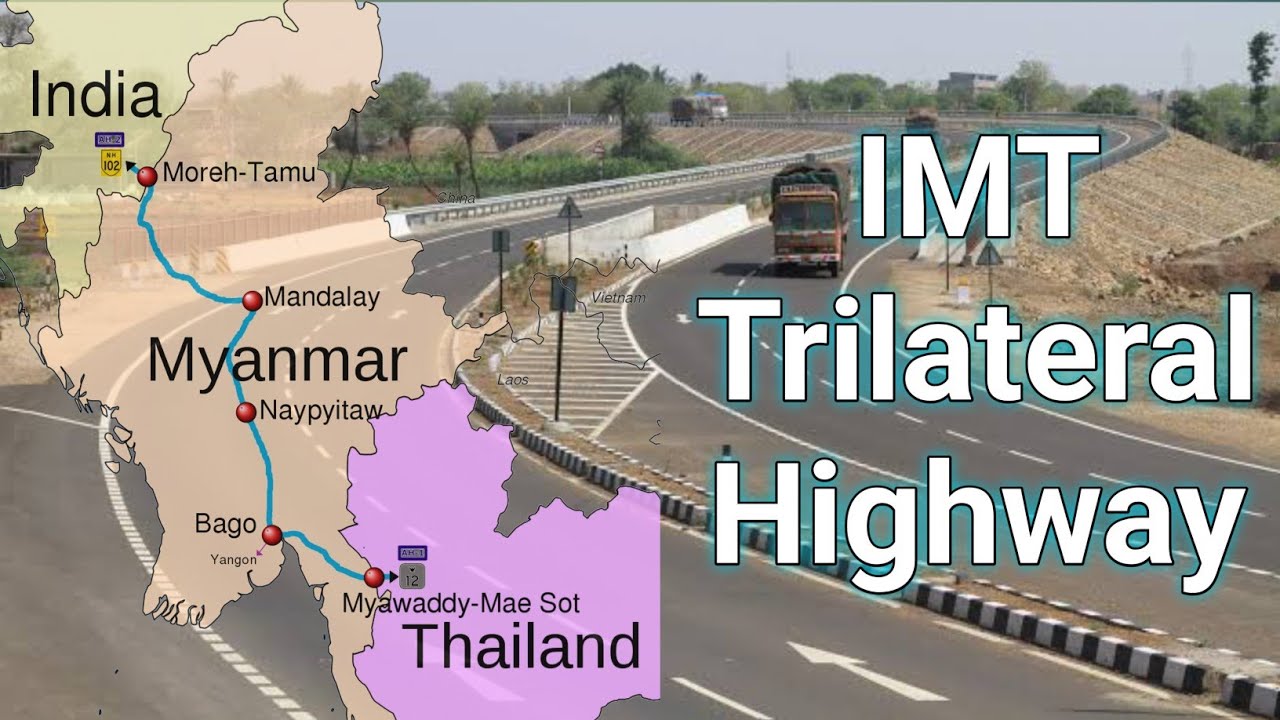
The Trilateral highway is an ambitious project between India, Myanmar and Thailand. The highway stretches from Moreh, Manipur in the Northeastern Indian state of Manipur and extends through Myanmar, ultimately reaching Mae Sot in Thailand. The highway covers a distance of approximately 1,360 kilometres (845 miles). The project is divided into several phases, with each country responsible for the construction and improvement of their respective segments. The highway's completion has been a gradual process, with some sections already operational while others are still under construction. It is also said that the highway is part of a larger plan to create a road network that will connect India to Southeast Asia, enhancing economic cooperation and cultural ties in the region where in the future, the Trilateral Highway is expected to be extended further into Laos, Cambodia, and Vietnam, creating an extended road network known as the "Asian Highway" or the "East-West Economic Corridor." The primary objective of this project is to facilitate the movement of goods and people between India and Southeast Asian countries. Furthermore, the project is expected to boost trade, tourism, and economic activities in the region. Additionally, it aims to promote regional integration and strengthen diplomatic ties between the three nations.
Thailand, as a key player in Southeast Asia, stands to benefit significantly from the Trilateral Highway. It offers improved access to Indian and Myanmar markets, enabling Thai businesses to expand and diversify their trade routes. Enhanced regional connectivity strengthens Thailand's position in trade initiatives, elevating its influence in the region. The highway's completion is expected to have a profound impact on the economies of India, Myanmar, and Thailand, opening up new markets and reducing transportation costs. Moreover, it improves land connectivity, facilitating the flow of goods, people, and services, playing a vital role in broader regional integration efforts.
Economic and Infrastructure Development in the Northeast Region
The Northeast region of India has its significance not only politically but also economically. The unique geographical features and landscape of the Northeastern region of India connect India with around five countries. These International borders surrounding the Northeastern Region of India played an important role as trade corridors throughout history. Before the advent of colonialism, the Northeast region had a primarily agricultural economy. Traditional agriculture, animal husbandry, and cottage industries like weaving and handicrafts were prevalent. The region's geography, characterized by hills, forests, and river valleys, shaped the economic activities of indigenous communities. Then came the British colonial rule, which had a significant impact on the economy of the Northeast. The region was incorporated into the British Empire through a series of treaties and administrative measures. The British introduced commercial agriculture, particularly tea cultivation in Assam, which became a major cash crop. The construction of railways and infrastructure projects aimed at extracting resources further integrated the region into the colonial economy.
In recent decades, there has been a concerted effort by the Indian government to improve infrastructure in the Northeast. This includes the construction of roads, bridges, airports, and railways to enhance connectivity within the region and with the rest of the country. Projects like the Trans-Arunachal Highway and the Bogibeel Bridge have been significant milestones in this regard. The Northeast region is also endowed with abundant hydroelectric potential. As a result, hydroelectric projects have been developed to harness this energy source for both regional consumption and export to other parts of India. Projects like the Subansiri Dam and the Dibang Dam are examples of this focus on hydroelectric power generation.
In past decades efforts have been made by the Indian government to promote trade and economic integration with neighbouring countries through initiatives like the Look East Policy (now Act East Policy). Border trade with countries like Nepal, Bangladesh, Bhutan, and Myanmar has been encouraged to leverage the region's strategic location. The highway would make it easier for tourists to travel between India and Southeast Asia, promoting tourism and cultural exchange. This could lead to an increase in tourism-related businesses and revenue. From a strategic perspective, the highway could provide India with greater access to the Bay of Bengal and the South China Sea, which are crucial for trade and security interests. The project could develop underdeveloped border regions in India, Myanmar, and Thailand, potentially reducing poverty and improving the living standards of local communities.
Stakeholders' perception of border trade through Trilateral Highway
There are several stakeholders involved in the India-Myanmar-Thailand Trilateral Highway ranging from the Government to Industries to local people. The stakeholders' perceptions of border trade through the India-Myanmar-Thailand Trilateral Highway can vary depending on their interests, roles, and experiences. The Governments of Participating Countries have viewed border trade through the Trilateral Highway as a means to promote economic development and regional integration. They see it as an opportunity to enhance trade relations, create jobs, and a mechanism to encourage people-to-people relations. Governments may also have concerns related to security, border management, and regulatory issues and various policies are put in place to ensure the smooth flow of goods and people while maintaining control over their borders.
There are wide range of industries involved such as Cross-Border Traders and Entrepreneurs, the Transport and Logistics Industry, International Investors and Financial Institutions and manufacturers etc. Cross-border traders and entrepreneurs are often the primary beneficiaries of increased trade along the highway. They may view it as a chance to expand their businesses, access new markets, and diversify their products. Transportation companies and logistics providers may see the Trilateral Highway as an opportunity to expand their operations and offer services to facilitate cross-border trade. International investors and financial institutions may view the highway as a potential investment opportunity. They may be interested in financing infrastructure projects and participating in trade-related ventures such as the JICA company which has been active in the region with infracture projects for over a decade now. Improved road infrastructure can boost trade between India and Southeast Asian countries, leading to economic growth and job creation. It would also provide easier access to the large and growing Southeast Asian market for Indian businesses. International investor's and financial institutions' perceptions will also be influenced by the political and economic stability of the region and the potential favourable return on investment.
Local communities living along the highway may perceive border trade as a source of livelihood and income. It can create opportunities for small-scale traders, farmers, and service providers. However, some communities may have concerns about the potential social and environmental impacts of increased trade, such as land displacement or changes in their way of life. That’s where the Environmental and conservation organizations come in too as they may express concerns about the potential environmental impacts of the highway, such as deforestation, habitat destruction, or pollution. Regional organisations and international partners, such as ASEAN are in support of the initiatives that promote regional connectivity and economic cooperation such as the India-Myanmar-Thailand Trilateral Highway.
Stakeholder perceptions and interests can be diverse and complex. Effective governance, consultation, and coordination among these stakeholders are crucial to addressing their concerns, ensuring equitable benefits, and maximising the positive impact of border trade through the India-Myanmar-Thailand Trilateral Highway. Public-private partnerships, community engagement, and transparent decision-making processes can help build consensus and facilitate successful implementation.
Challenges
Constructing and maintaining the highway encounters numerous obstacles, ranging from rugged terrain to political intricacies, necessitating seamless cross-border coordination. Overcoming these hurdles is pivotal for the highway's effective completion and operation. The endeavour of establishing and upholding a transnational roadway across diverse landscapes poses substantial logistical and financial burdens, demanding significant investment in infrastructure development and upkeep. The following are breakdown of potential strategies to address each challenge:
Security Concerns:
- Implementing robust security measures along the highway route, including increased surveillance, checkpoints, and cooperation with local security forces.
- Engaging in transparent communication and consultation with neighbouring countries to address any apprehensions and build trust.
- Conducting risk assessments and developing contingency plans for potential security threats.
- Engaging with local communities to address underlying issues contributing to insecurity.
Environmental Impact:
- Conducting thorough environmental impact assessments (EIAs) and implementing mitigation measures to minimize ecological damage.
- Investing in sustainable construction practices, such as using eco-friendly materials and minimizing habitat disruption.
- Implementing reforestation and habitat restoration initiatives in affected areas.
Political and Administrative Challenges:
- Establishing a joint task force or coordinating body comprised of representatives from each country to streamline decision-making and address administrative hurdles.
- Engaging in diplomatic efforts to resolve disputes and promote cooperation among participating nations.
- Facilitating dialogue between stakeholders at various levels to ensure alignment on project goals and objectives.
Economic Disparities and Economic Viability:
- Implementing targeted development programs aimed at promoting inclusive growth and addressing disparities in wealth and opportunity.
- Investing in infrastructure and capacity-building initiatives in economically marginalized regions to unlock their potential for economic participation.
- Conducting thorough feasibility studies and cost-benefit analyses to assess the project's economic viability.
- Exploring innovative financing mechanisms, such as public-private partnerships and multilateral funding, to support the project's construction and maintenance costs.
Regulatory and Legal Framework:
- Harmonizing regulatory frameworks and trade agreements among participating countries to facilitate seamless cross-border trade and transit.
- Establishing dispute resolution mechanisms to address legal challenges and conflicts that may arise during project implementation.
Maintenance and Sustainability:
- Investing in regular maintenance and upkeep of the highway infrastructure to ensure its long-term sustainability.
- Developing disaster preparedness and response plans to mitigate the impact of natural disasters on the highway's operation.
Ultimately, the highway holds immense promise in bolstering regional connectivity, trade, and economic development. However, it must surmount myriad challenges, spanning infrastructure, security, environmental, and political domains. Success hinges on meticulous planning, substantial investment, and robust cooperation among involved nations. Triumphing over these challenges necessitates diligent planning, international collaboration, and unwavering commitment from all stakeholders. By addressing these challenges through collaborative efforts and innovative solutions, the India-Myanmar-Thailand Trilateral Highway project can realize its potential as a catalyst for regional connectivity and economic development.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the India-Myanmar-Thailand Trilateral Highway project represents a significant milestone in regional connectivity and economic integration efforts. With its ambitious goal of linking India to Southeast Asia through enhanced land connectivity, the highway holds the promise of fostering economic growth, facilitating cross-border trade, and strengthening diplomatic ties among the participating nations. However, the realisation of these benefits is contingent upon overcoming a myriad of challenges spanning security, environmental, political, regulatory, and economic domains.
Security concerns along the highway route necessitate robust measures to safeguard against potential threats, while environmental impact assessments and sustainable construction practices are vital to mitigate ecological damage. Addressing political and administrative challenges requires coordinated efforts and diplomatic engagement among the involved nations, coupled with transparent communication and consultation with stakeholders. Furthermore, efforts to bridge economic disparities and navigate geopolitical sensitivities are essential to garnering broad-based support for the project.
Moreover, establishing a harmonized regulatory and legal framework, ensuring the long-term maintenance and sustainability of the highway infrastructure, and assessing its economic viability through thorough feasibility studies are imperative steps toward realizing the project's potential benefits. Public-private partnerships, innovative financing mechanisms, and multilateral cooperation are key enablers in overcoming these challenges and ensuring the successful implementation of the Trilateral Highway project.
In essence, while the Trilateral Highway project holds immense promise as a catalyst for regional connectivity and economic development, its success hinges upon the concerted efforts, unwavering commitment, and collaborative spirit of all stakeholders involved. By addressing the identified challenges through proactive planning, international cooperation, and innovative solutions, the project can emerge as a transformative force in fostering closer ties, enhancing trade relations, and promoting inclusive growth across the region. Overall, the Trilateral Highway represents a silver lining for India, Myanmar, and Thailand by fostering economic development, regional integration, and diplomatic ties among the three countries.
References:
https://infra.economictimes.indiatimes.com/news/roads-highways/india-myanmar-thailand-trilateral-highway-progress-update/101984181#
https://www.orfonline.org/expert-speak/enhancing-connectivity-and-regional-integration/#
https://currentaffairs.adda247.com/india-myanmar-thailand-trilateral-highway-project/
https://testbook.com/ias-preparation/india-myanmar-thailand-trilateral-highway
https://www.insightsonindia.com/2023/07/04/india-myanmar-thailand-trilateral-highway-2/
"Written By Ms. Ngawang Gamtso Hardy"
Economic Analyst, Deputy Editor-in-Chief
Royal Thai Embassy














